The 5 Essential Pillars of a Powerful, Sustainable Business
Related Articles: The 5 Essential Pillars of a Powerful, Sustainable Business
- 5 Essential Business Management Skills For Unstoppable Success
- 5 Unstoppable Strategies For Explosive Business Growth
- 7 Ways to foster Your Business You Would prefer not to Overlook: Business Systems To Effectively Execute Now
- 5 Unstoppable Strategies For Explosive Business Growth
- 12 Strong Strides To Home Business Achievement
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The 5 Essential Pillars of a Powerful, Sustainable Business. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
The 5 Essential Pillars of a Powerful, Sustainable Business

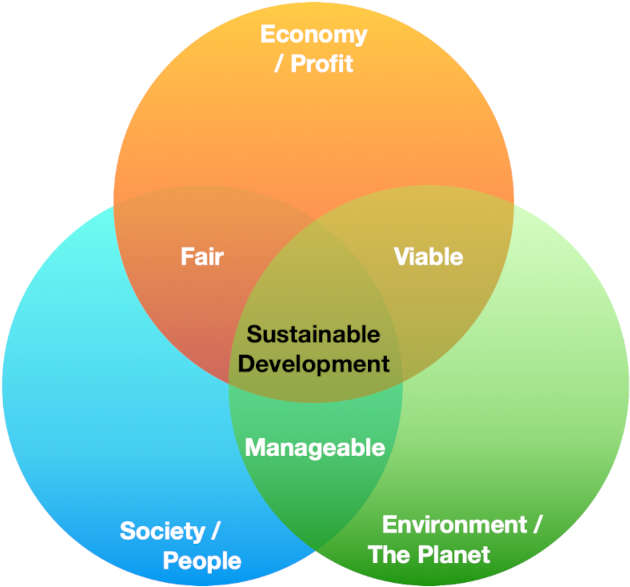
The world is facing a climate crisis, and businesses have a critical role to play in finding solutions. Sustainability is no longer a nice-to-have; it’s a necessity for long-term success. Companies that embrace sustainable practices are not only contributing to a healthier planet, but also building a more resilient and profitable future.
This article will delve into the five essential pillars of a powerful, sustainable business, exploring how companies can integrate sustainability into their core operations and drive positive change.
1. Environmental Responsibility:
At the heart of sustainable business lies environmental responsibility. This encompasses reducing a company’s environmental footprint across its entire value chain, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing, distribution, and end-of-life management.
a) Reducing Emissions:
Greenhouse gas emissions are a major contributor to climate change. Companies can reduce their emissions by:
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources: Solar, wind, and hydropower offer clean and sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels.
- Improving energy efficiency: Implementing energy-saving measures in buildings, equipment, and processes can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Optimizing transportation: Choosing efficient modes of transport, reducing travel distances, and exploring electric vehicles can minimize emissions from logistics.
b) Managing Waste:
Waste generation is a significant environmental challenge. Companies can adopt strategies to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization:
-
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Implementing a comprehensive waste management program that prioritizes reducing waste at the source, reusing materials, and recycling whenever possible.

- Circular Economy Principles: Embracing a circular economy model, where materials are kept in use for as long as possible, reducing waste and maximizing resource efficiency.
- Composting: Utilizing organic waste for composting, returning valuable nutrients to the soil and reducing landfill waste.
c) Water Conservation:
Water scarcity is a growing concern. Companies can implement water conservation measures:
- Reducing water usage: Implementing efficient irrigation systems, minimizing water use in manufacturing processes, and encouraging water-saving practices in offices.
- Water recycling and reuse: Utilizing treated wastewater for non-potable uses like irrigation and cleaning.
- Protecting water resources: Advocating for responsible water management practices and supporting initiatives that protect water sources.
2. Social Responsibility:
Sustainable businesses recognize their responsibility to contribute to the well-being of their employees, communities, and society as a whole.
a) Ethical Labor Practices:
- Fair Wages and Benefits: Ensuring fair and competitive wages, offering benefits like health insurance and retirement plans, and promoting employee well-being.
- Safe and Healthy Work Environment: Providing a safe and healthy workplace, implementing robust safety protocols, and addressing potential risks proactively.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Promoting a diverse and inclusive workforce, fostering a culture of respect and equal opportunities for all employees.
b) Community Engagement:
- Supporting Local Communities: Investing in local communities through initiatives like job creation, community development programs, and partnerships with local organizations.
- Transparency and Accountability: Being transparent about their operations and practices, engaging with stakeholders, and being accountable for their social and environmental impact.
- Ethical Sourcing: Ensuring that all materials and products are sourced ethically and responsibly, respecting human rights and labor standards throughout the supply chain.
c) Human Rights:
- Respecting Human Rights: Upholding human rights throughout their operations and supply chains, including the rights of workers, consumers, and local communities.
- Addressing Human Rights Issues: Proactively identifying and addressing potential human rights risks and developing strategies to mitigate them.
- Promoting Human Rights Standards: Supporting and advocating for international human rights standards and working to improve labor conditions in their industry.
3. Economic Sustainability:
Sustainable businesses understand that financial viability is essential for long-term sustainability.
a) Long-Term Profitability:
- Investing in Innovation: Continuously investing in research and development to create innovative products and processes that drive growth and sustainability.
- Developing Sustainable Products and Services: Offering products and services that are environmentally friendly, resource-efficient, and meet the evolving needs of consumers.
- Building a Resilient Business: Adapting to changing market conditions, managing risks proactively, and building a business model that is resilient to disruptions.
b) Responsible Financial Practices:
- Transparent Financial Reporting: Providing transparent and comprehensive financial reporting, disclosing their environmental and social performance.
- Ethical Investments: Investing in projects and companies that align with their sustainability values and contribute to a positive social and environmental impact.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating financial risks associated with environmental and social factors, including climate change, resource scarcity, and social unrest.
c) Inclusive Growth:
- Creating Economic Opportunities: Promoting inclusive economic growth by creating jobs, supporting small businesses, and empowering marginalized communities.
- Fair Trade Practices: Engaging in fair trade practices, ensuring fair prices for suppliers and workers, and promoting equitable distribution of benefits.
- Sustainable Supply Chains: Building sustainable supply chains that minimize environmental impact, promote ethical labor practices, and ensure the well-being of all stakeholders.
4. Governance and Transparency:
Strong governance and transparency are crucial for building trust and ensuring accountability.
a) Ethical Leadership:
- Strong Corporate Governance: Implementing strong corporate governance structures, ensuring accountability and transparency in decision-making.
- Ethical Leadership: Embracing ethical leadership principles, promoting integrity, and setting a high standard for conduct within the organization.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with stakeholders, including employees, investors, customers, suppliers, and communities, to gather feedback and build consensus.
b) Transparency and Disclosure:
- Reporting on Sustainability Performance: Providing transparent and comprehensive reports on their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Establishing robust data collection and analysis systems to track their sustainability progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Third-Party Verification: Seeking independent third-party verification of their sustainability claims to enhance credibility and accountability.
c) Collaboration and Partnerships:
- Building Partnerships: Collaborating with other businesses, NGOs, and government agencies to advance sustainability goals and share best practices.
- Industry-Wide Initiatives: Participating in industry-wide initiatives to drive collective action and promote sustainable practices across the sector.
- Advocating for Policy Change: Advocating for policies that support sustainability and create a level playing field for businesses committed to responsible practices.
5. Innovation and Continuous Improvement:
Sustainable businesses are constantly striving to improve their practices and find new ways to reduce their impact and create positive change.
a) Embracing Innovation:
- Investing in Sustainable Technologies: Investing in research and development to develop and deploy sustainable technologies that improve efficiency, reduce emissions, and minimize waste.
- Developing Circular Economy Solutions: Implementing circular economy principles throughout their operations, from product design to end-of-life management.
- Empowering Employees: Encouraging employees to be innovative and contribute ideas for improving sustainability practices.
b) Continuous Improvement:
- Setting Ambitious Targets: Setting ambitious sustainability targets and tracking progress regularly to ensure continuous improvement.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Using data and analytics to identify areas for improvement and optimize sustainability performance.
- Learning from Best Practices: Learning from other companies and organizations that are leading the way in sustainability.
Conclusion:
Building a powerful, sustainable business is a journey, not a destination. It requires a commitment to continuous improvement, innovation, and collaboration. By embracing these five pillars, companies can create a more sustainable future for their businesses, their communities, and the planet.
Image:
Note: The image used in this article is a placeholder and can be replaced with an image that better represents the content.
Word Count: 1614 words
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The 5 Essential Pillars of a Powerful, Sustainable Business. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Sponsored Website: paid4link.com











